Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
图: 1 / 1
CD209a Antibody (17-2092-82) in Flow

产品信息
17-2092-82
种属反应
已发表种属
宿主/亚型
分类
类型
克隆号
偶联物
激发/发射光谱
形式
浓度
纯化类型
保存液
内含物
保存条件
运输条件
RRID
产品详细信息
Description: The LWC06 antibody was generated by immunization with the recombinant extracellular region of mouse CIRE/DC-SIGN (CD209). CIRE/DC-SIGN was identified by its expression on CD8 alpha- dendritic cells and plasmacytoid predendritic cells, and is the closest homologue of human DC-SIGN. Human DC-SIGN was originally identified in human placenta for its ability to bind the HIV envelope protein gp120 in a CD4-independent manner. CIRE/DC-SIGN is a 33 kDa type II transmembrane C-type lectin protein. It contains a C-terminal, extracellular, Carbohydrate Recognition Domain (CRD) that is predicted to bind mannose and other carbohydrates in a calcium dependent manner. It has been postulated that CIRE/DC-SIGN may play a role in T-dendritic cell interactions through binding with members of the ICAM family. CIRE/DC-SIGN is differentially expressed by sub-populations of dendritic cells and preliminary data suggest that its expression varies depending on the activation state of the host. CIRE/DC-SIGN is down-regulated in spleen-derived dendritic cell cultures supplemented with GM-CSF. While human DC-SIGN is predominantly expressed in dendritic cells, CIRE/DC-SIGN mRNA has also been detected in B cells. The LWC06 monoclonal antibody does not cross-react with the closely related SIGNR1, SIGNR2, SIGNR3 or SIGNR4.
CD209 protein is sensitive to collagenase treatment.
Applications Reported: This LWC06 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis.
Applications Tested: This LWC06 antibody has been tested by flow cytometric analysis of transfected cell line. This can be used at less than or equal to 0.25 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
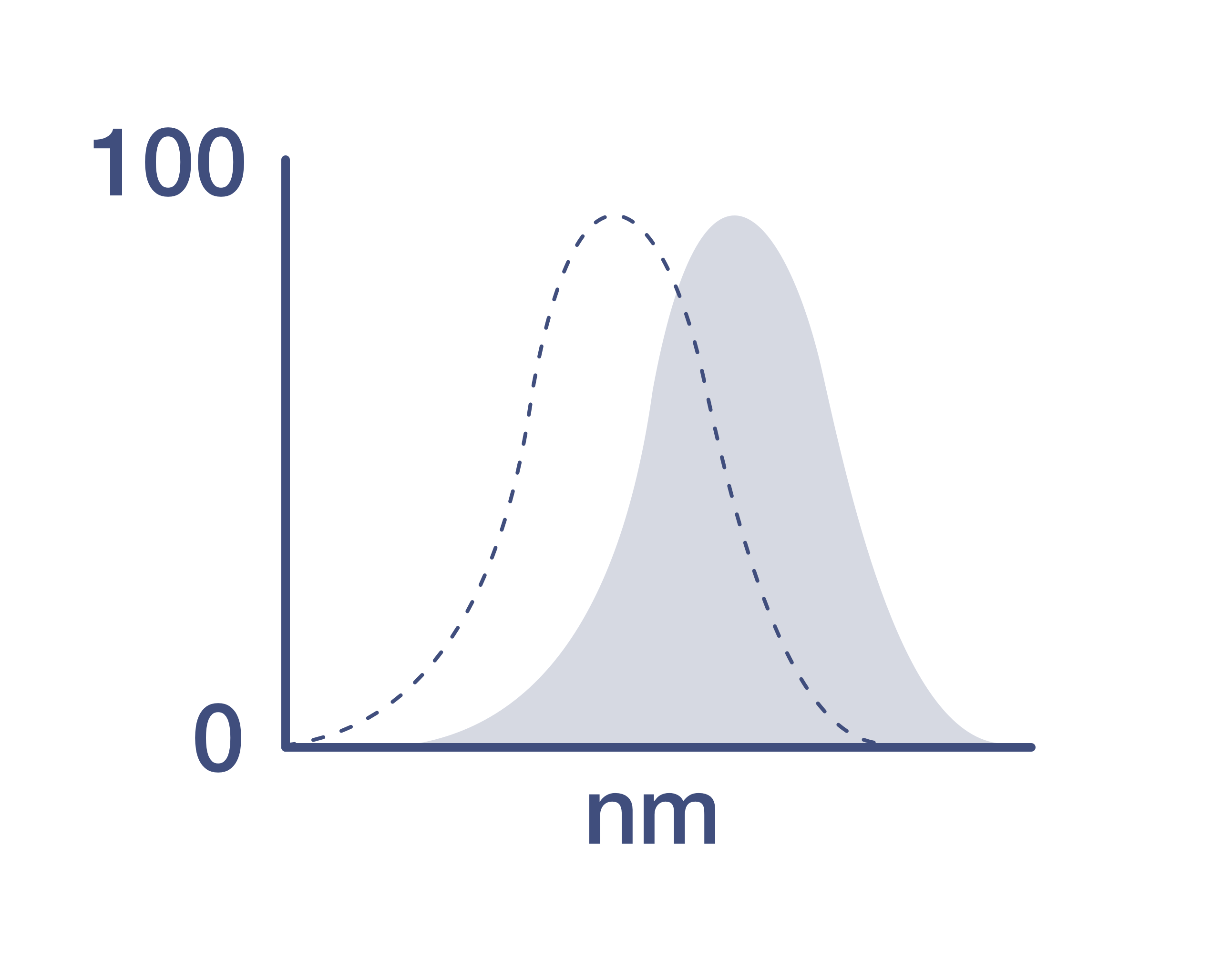
Excitation: 633-647 nm; Emission: 660 nm; Laser: Red Laser.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
靶标信息
This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and is often referred to as DC-SIGN because of its expression on the surface of dendritic cells and macrophages. The encoded protein is involved in the innate immune system and recognizes numerous evolutionarily divergent pathogens ranging from parasites to viruses with a large impact on public health. The protein is organized into three distinct domains: an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a tandem-repeat neck domain and C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. The extracellular region consisting of the C-type lectin and neck domains has a dual function as a pathogen recognition receptor and a cell adhesion receptor by binding carbohydrate ligands on the surface of microbes and endogenous cells. The neck region is important for homo-oligomerization which allows the receptor to bind multivalent ligands with high avidity. Variations in the number of 23 amino acid repeats in the neck domain of this protein are rare but have a significant impact on ligand binding ability. This gene is closely related in terms of both sequence and function to a neighboring gene (GeneID 10332; often referred to as L-SIGN). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN differ in their ligand-binding properties and distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants.
仅用于科研。不用于诊断过程。未经明确授权不得转售。
How to use the Panel Builder
Watch the video to learn how to use the Invitrogen Flow Cytometry Panel Builder to build your next flow cytometry panel in 5 easy steps.
生物信息学
蛋白别名: CD209; CD209 antigen-like protein A; DC-SIGN; Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin; MGC129965; MGC130443
基因别名: CD209; Cd209a; CDSIGN; CIRE; DC-SIGN; DC-SIGN1; Dcsign; SIGN-R1; SIGNR5
UniProt ID: (Mouse) Q91ZX1
Entrez Gene ID: (Mouse) 170786